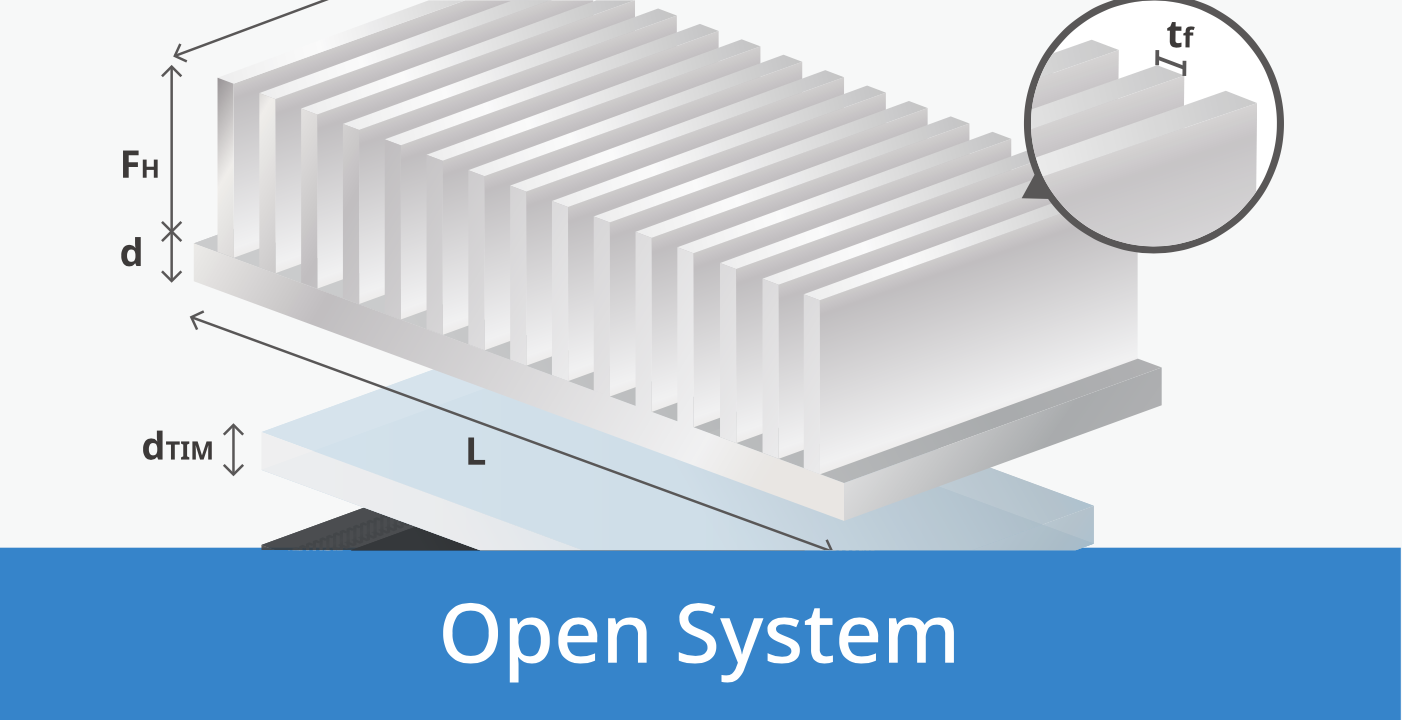
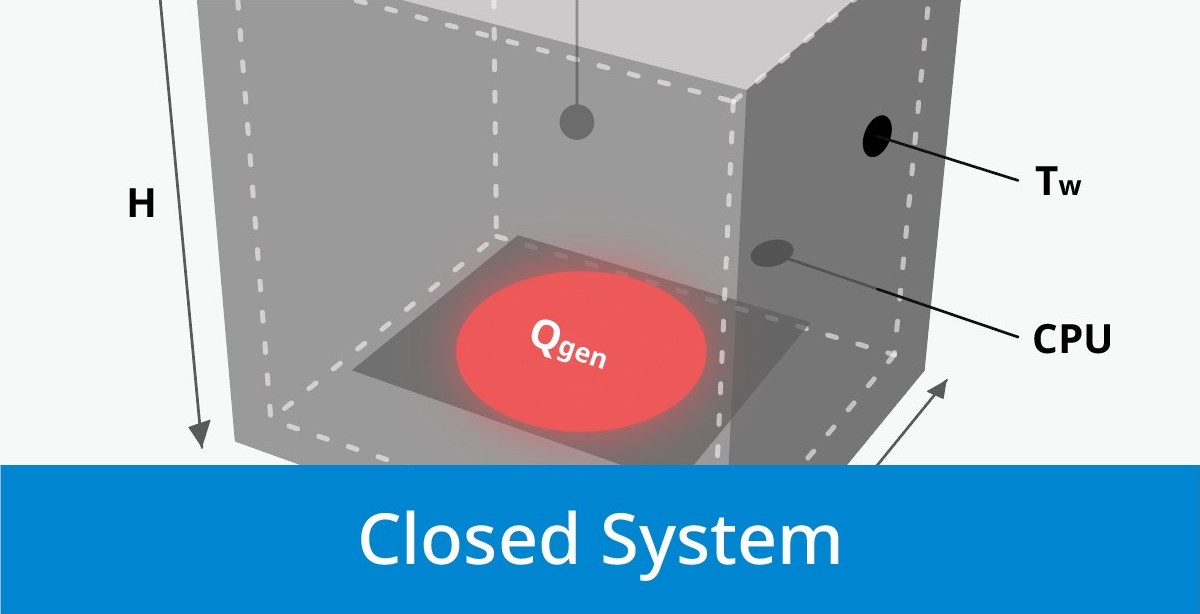
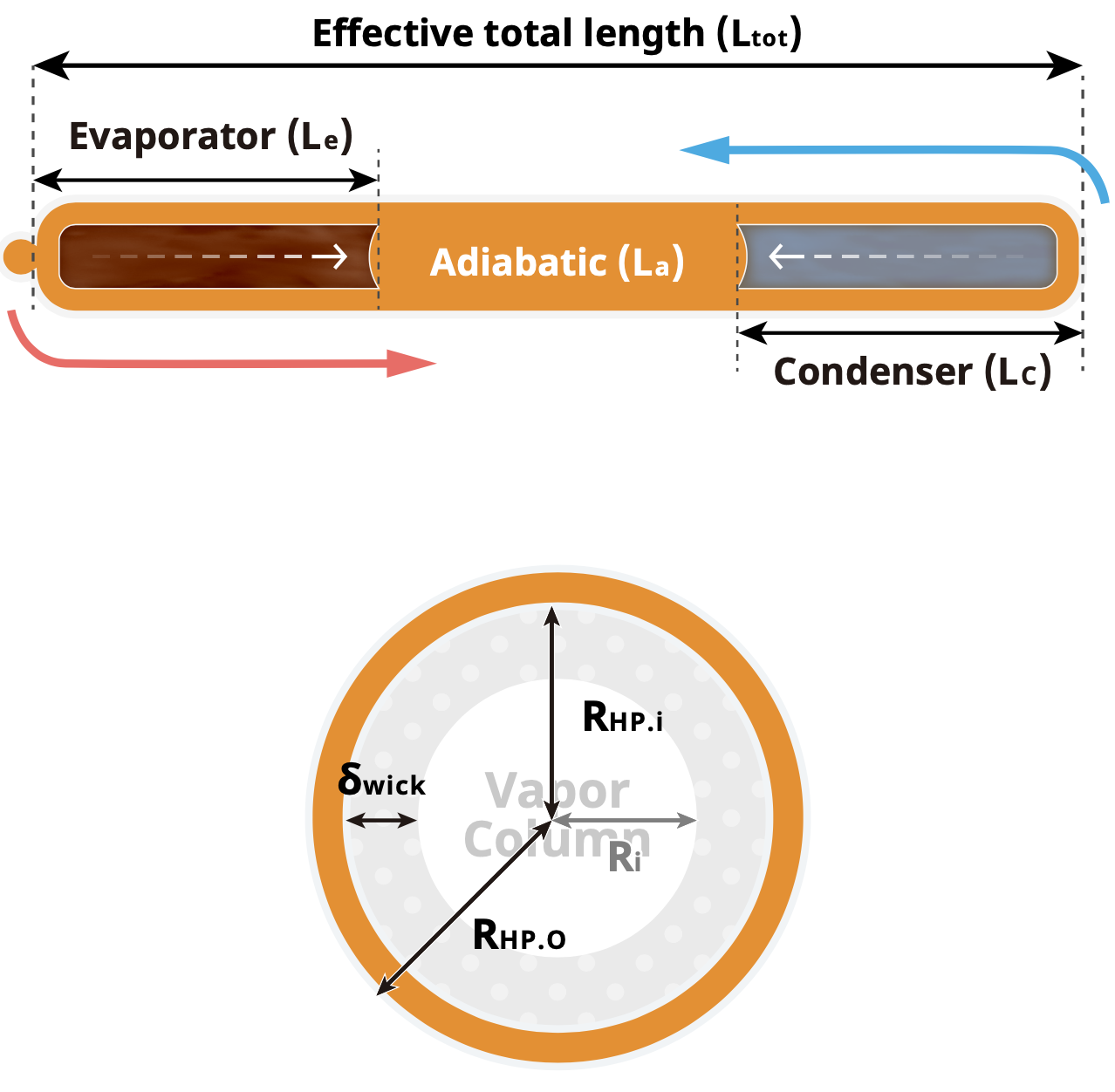
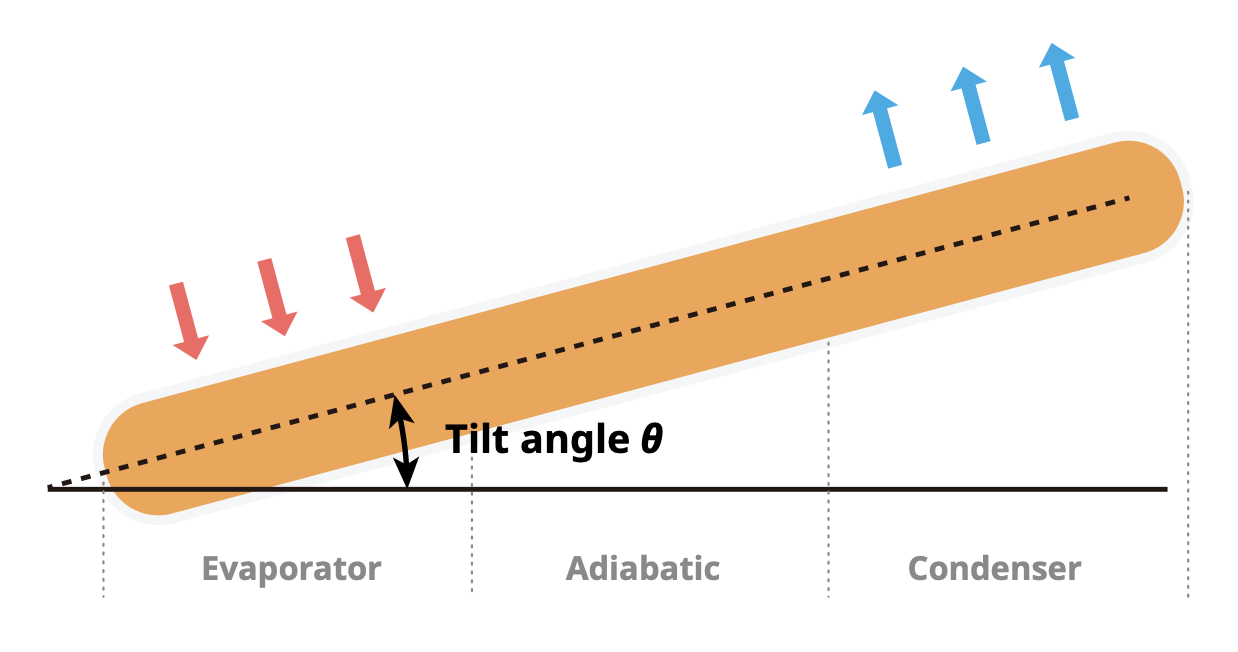
(A) Geometry Parameter of Heat Pipe
The geometric parameters of the heat pipe include the effective total length of the heat pipe (Ltot), the length of the evaporation section (Le), length of the condensation section (Lc), the inner diameter of the heat pipe (RHP.i), the outer diameter of the heat pipe (RHP.O), the thickness of capillary wick structure (δwick), etc.;
(B) Wick Structure Parameters of Heat Pipe
Wick structure parameters include porosity (ε), porous radius (rw), and permeability (Kw).
The purpose of this simulation is to focus on the change of Qmax(calculate) when the heat pipe geometry parameter is changed.
The friction process coefficient f', an indicator of the quality of the user's manufacturing process technology for heat pipes. If the user already knows the experimental value Qmax(exp), then Qmax(exp) can be the same as Qmax(calculate) by adjusting f'. One thing should be notice that once f' is adjusted, then f' is fixed until the manufacture process is changed. f' is a parameter that cannot be changed in the same manufacturing process. If you don't know the Qmax(exp), then f'=800 will be used as the default value for the general heat pipe.
(C) Operating Condition
Operating condition includes the operating temperature (Top) and its corresponding working fluid thermodynamic properties, which have the density, viscosity, specific volume, specific heat, and enthalpy.
Calculation
| Heat Pipe | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adiabatic Length | La | mm | |
| Wall thickness of Heat Pipe | δwall | mm | |
| Radius of vapor column | Ri | mm | |
| Cross section area of wick structure | Aw | m2 | |
| Cross section area of vapor column | Ai,c | m2 | |
| Maximum heat transport of heat pipe | Qmax,Top | W |